Introduction
5W2H is a highly useful technique for describing problems, particularly effective in problem-solving methods such as 8D, PDCA, A3, Global 8D (G8D), or DMAIC. This technique allows for a more detailed problem description, which is crucial for establishing interim containment actions and identifying root causes.
In this article, we will introduce the 5W2H concept, present two practical examples, and discuss the advantages and disadvantages of this technique.
The Problem of ..The Problem Description..
Problem-solving requires identifying the root causes of a problem. It is not easy; it can be hard or even very hard. Unfortunately, we often attempt to solve problems based on insufficient information received from our customers or colleagues.
Individuals involved in corrective actions (e.g., handling complaints or improving process quality) frequently face the challenge of imprecise problem descriptions. How often have you had to take urgent action based on such "comprehensive" information as:
- The product doesn't work.
- Lacks functionality.
- The product failed the functional test.
Solving a problem based on such generalities is nearly impossible. Therefore, it's worth implementing the 5W2H technique. Its application allows for better problem description, deeper understanding, and a higher likelihood of effective root cause analysis. As a result, 5W2H enables faster and more efficient problem resolution.
The 5W2H Concept
The 5W2H technique is based on seven key questions: five beginning with the letter W (What, Why, Who, Where, When) and two with the letter H (How, How Many), hence the acronym 5W2H. Below is the meaning of each "W" and "H":
- WHO. Who reported the problem? Who does it affect? This could be a specific customer, supplier, or internal department.
- WHAT. What is the problem? Precisely describe the phenomenon, including part numbers, defect descriptions, photos illustrating the issue, and other critical information.
- WHEN. When did the problem appear? Precise time data, such as the date and time, can be critical for narrowing down potential causes.
- WHERE. Where did the problem occur? It could be a geographical location (e.g., country, city) or a facility, production line, station, etc.
- WHY. Why is this phenomenon a problem? What are its effects?
- HOW. Under what circumstances did the problem occur? How was it detected?
- HOW MANY. What is the scale of the problem? How many cases occurred? How many products are affected?
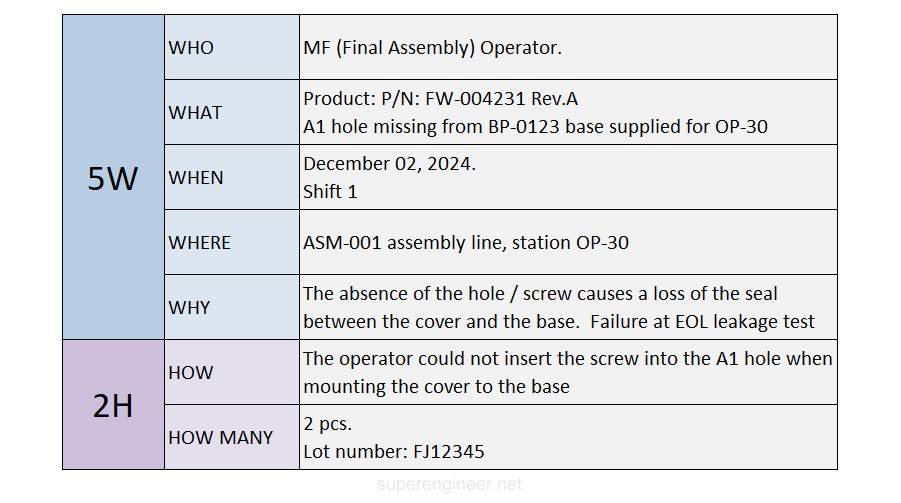
5W2H Example
The following are two examples of the application of the 5W2H technique in two different cases:

Advantages of 5W2H
- Simplicity. The method is intuitive and does not require advanced or specialized tools.
- Comprehensiveness. It provides a multidimensional view of the problem (description, who it affects, when it occurred, how many units, etc.).
- Versatility. It can be used in any industry and within various problem-solving methods (8D, G8D, PDCA, DMAIC, etc.).
- Improved Communication. Thanks to an organized problem description, it is easier to communicate the issue to a team, client, or supplier.
- Time Savings. Applying the 5W2H method helps reduce problem-solving time. A precise description narrows down potential causes, allowing time and energy to focus on analyzing the most likely ones.
Disadvantages of 5W2H
- Time-Consuming Data Collection. Providing detailed information for each 5W2H question can sometimes feel labor-intensive.
Various Variations
We can encounter different "W" questions (Who, What, When, Where, Why) and "H" questions (How, How Many, How Big, How Much) in the context of problem descriptions. In business practice, various combinations of "W" and "H," as well as other designations, are used. For example:
- 5W2H: Who, What, Where, When, Why, How, How Many.
- 5W1H: Who, What, Where, When, Why, How.
- Global 8D: What, Where, When, How Big.[1]
- VDA 8D: What, Where, When, Scope.[2]
- AIAG CQI-20: What, Where, When, How Big.[3]
- Kepner-Tregoe (KT): What, Where, When, Extent.[4]
Modifying the "W" and "H" questions based on the context allows the technique to be tailored to the specific requirements of a given industry or project. This makes the problem description easier to apply in a particular situation.
Different interpretations of the meaning of some questions (especially WHY) may arise. I recommend clearly defining the meaning of each question within your organization to ensure a systematic and standardized approach.
Conclusion
5W2H is a practical and universal tool for precisely describing problems in methods such as 8D, G8D, PDCA, or DMAIC. With seven simple questions, it is possible to quickly understand key aspects of the problem, regardless of the industry.
Using 5W2H significantly accelerates and simplifies problem-solving. A precise description allows for narrowing down potential causes, which shortens the analysis time.
Furthermore, consider combining 5W2H with the Is / Is Not technique, which complements problem descriptions perfectly.
Footnotes
- Ford Motor Corp., Global 8D Reference Guide, 2018.
- Verband der Automobilindustrie e. V. (VDA), 8D - Problem Solving in 8 Disciplines, 1st ed., 2018.
- AIAG, CQI-20 Effective Problem Solving, 2nd ed., 2018.
- https://kepner-tregoe.com/



